Virginia
Type |
Symbol |
Year Est. |
|---|---|---|
State Rock |
Nelsonite |
2016 |
State Fossil |
Chesapecten jeffersonius |
1993 |
State Rock: Nelsonite
State Fossil: Chesapecten jeffersonius
References
https://statesymbolsusa.org/states/united-states/virginia
Geology of Virginia's National Parks
Through Pictures
(at least the one's I have been to)
Assateague Island National Seashore
National Parks visited but I have no pictures (at this time) to do a geology post
(link directs to NPS site)
Arlington House, The Robert E. Lee Memorial (2002)
Blue Ridge Parkway (2003)
Colonial National Historical Park (1994)
George Washington Memorial Parkway (2002)
Assateague Island National Seashore
Visited in 2002
.jpg)
For all of the pictures from Assateague Island National Seashore be sure to head over to the:
Visited in 1994 and 2002
Much like the Great Smoky Mountains to the south, Shenandoah is formed by a small part of the Appalachian Mountains.
.jpg)
The Appalachian Mountains are an amazing mountain belt because you can easily see the geology any time you pull up an aerial image of the region (like in Google Earth).
Google Earth aerial imagery of the central eastern US
The flow of the mountains from central Pennsylvania through western Virginia (where Shenandoah is located) to eastern Tennessee and western North Carolina is a perfect visual for the impact that produced them when North America collided with Africa. However, there are some events that took place before the Appalachian Mountains were formed.
.jpg)
Granodiorites of the Pedlar Formation at the Hazel Mountain Overlook
As was the case for the Great Smoky Mountains, the oldest rocks within Shenandoah National Park are about 1.1 billion years old. These rocks formed during what is known as the Grenville Event and are known in the park as the Old Rag Granite and a gneiss called the Pedlar Formation (pictured above), The Grenville Event was the mountain building event (orogeny) which occurred during the formation of the Rodinia Supercontinent.
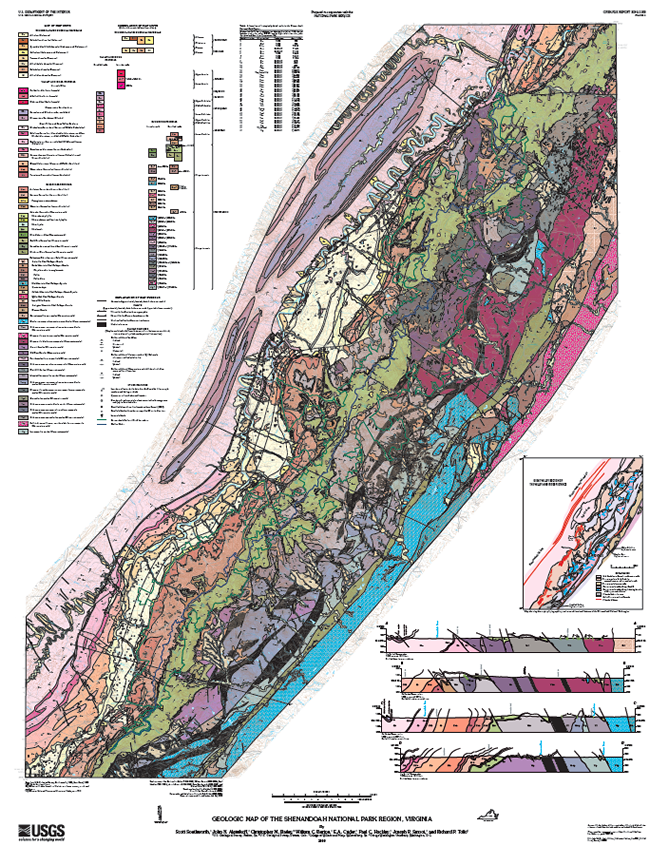
Geological map of Shenandoah National Park. Full size available on the USGS website.
The Pedlar Formation and the Old Rag Granite make up the majority of the outcrops through the central portion of the park.
.jpg)
Big Meadows
As Rodinia started to split apart, or rift, lava poured out, forming the Catoctin Formation which is made up primarily of a metamorphosed basalt known as greenstone. The rifting continued until there was an ocean separating North America from Africa, much like today. This ocean is known to geologists as the Iapetus Ocean. Because of the hardness of the Catoctin Formation and its location within the park, many of the waterfalls are formed flowing over this formation. Big Meadows, as seen in the picture above, is located right atop 1,800 feet thick deposits of the Catoctin Formation. Along the edge of Big Meadows is Dark Hollow Falls, which drains the meadows as it falls over the Catoctin Formation.
.jpg)
Erosion of the Grenville Mountains produced sediments that were deposited within the Iapetus Ocean, forming the rocks that would later make up much of the Appalachian Mountains. These include Cambrian and Ordovician age limestones, sandstones, and mudstones. Then around 470 million years ago, during the Ordovician, the continents took an about face and started to head towards one another again.
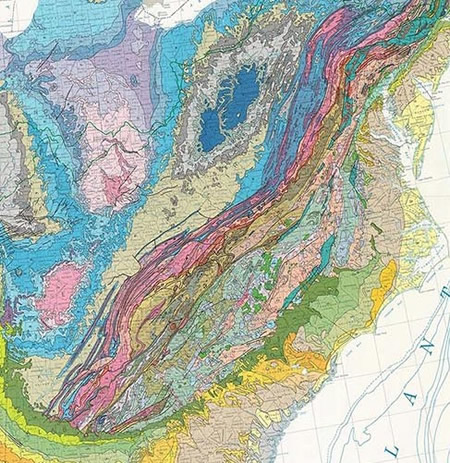
Geologic map of the eastern US. Image courtesy of geologictimepics.com.
This eventually ended when North America plowed into Africa creating Pangea, the next in the supercontinent line. This collision uplifted the Appalachian mountains and created the great mountain imagery as we can see in the aerial and geological map above. Around 200 million years ago, in the Jurassic, Pangea started to break apart, creating the Atlantic ocean as well as eventually putting the continents in the configuration as we know them today. During the breakup, several Jurassic age dikes, volcanic intrusions, were formed and can also be seen in various locations within the park. Over time the Appalachian Mountains had slowly eroded to shadows of their former glories but the former grandeur of of them can still be glimpsed in the aerial imagery.
References
https://www.usgs.gov/geology-and-ecology-of-national-parks/geology-shenandoah-national-park
https://geologictimepics.com/2020/03/27/touring-the-geologic-map-of-the-united-states/
http://www.virginiaplaces.org/geology/rocksdui2.html
http://npshistory.com/publications/geology/state/va/vdmr-bul-86/appendix.htm