-Stage 2.1-
Folds
There are many types of fold that a geologist could study. These include:
You should also be aware of how to name folds.
But before going into those, you need to understand some basic geologic map skills.
Geologic Rock Units
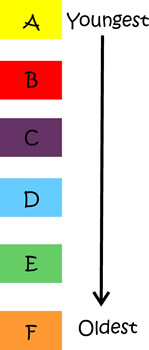
-
The list on the right is representative of a geologic map legend
-
Rocks on maps are listed in age order
-
The rocks on the top of the list are the youngest
-
The one's on the bottom are the oldest
-
This resembles real-life where rocks are deposited, then the "younger rocks" are deposited later on top of them
-
These rock units will be used in the proceeding pictures.
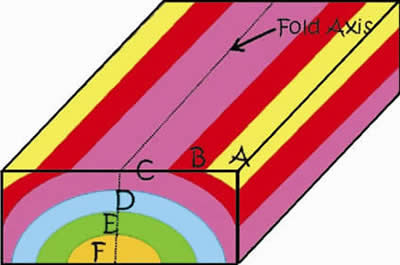
-
A fold in the rocks resulting in an "A" shape (A for Anticline)
-
The top side of the box on the left represents the Earth's surface
-
The front of the box shows the type of fold
-
The dotted line represents the "fold axis"
-
The resulting fold has the oldest rocks in the center
-
Then rocks repeat on both side of the center symmetrically
-
The width of the units on the surface are equal on both sides of the center unit.
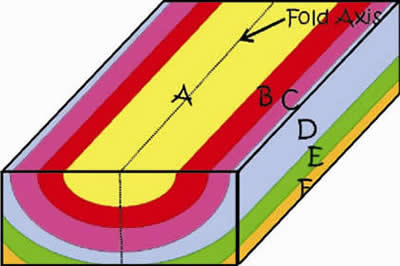
-
A fold in the rocks resulting in a "U" shape
-
The top side of the box on the left represents the Earth's surface
-
The front of the box shows the type of fold
-
The dotted line represents the "fold axis"
-
The resulting fold has the youngest rocks in the center
-
Then rocks repeat on both side of the center symmetrically
-
The width of the units on the surface are equal on both sides of the center unit
Plunging Syncline
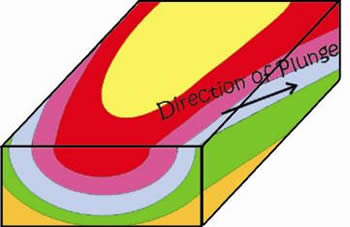
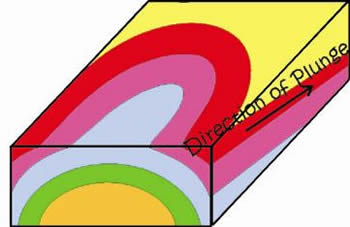
Plunging Anticline
-
The direction of plunge is visible along the side of the blocks
-
This changes the symmetrical pattern seen along the surface
-
The new pattern is giant curves on the earths surface
-
The "arrow" pattern points in the direction of plunge in an anticline
-
The "arrow" points in the opposite direction in a syncline
Non-Symmetrical Anticline
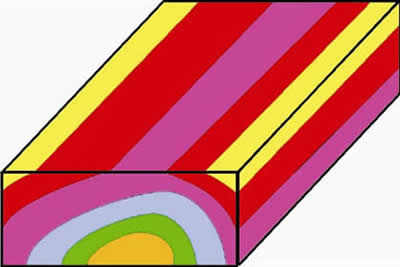
-
Non-symmetrical folds cause the same rock units to be different widths on either side of the fold axis
-
On the surface, Synclines and Anticlines will both have the unequal unit widths in non-symmetrical folds
-
On the surface, the side with the thinner outcroppings overlie the steeper portion of the fold
When identifying folds there are 3 types of qualifiers that would normally be used for a complete description:
Anticline or Syncline
Symmetrical or Non-symmetrical
Plunging or Non-plunging
(typically you don't say "non-plunging", you would just leave off that term)
Examples:
Plunging Symmetrical Anticline
Non-symmetrical Syncline
